Introduction
In engineering, drawing reviews are key to maintaining design integrity and project success. Engineering drawings are critical documents that outline specifications, dimensions and material requirements for construction. An error in these technical drawings can mean delays, safety issues and added cost. So a thorough review is needed to catch discrepancies, misinterpretations and compliance issues. Manual reviews can be time consuming and prone to oversight, that’s why AI driven tools, including GPT models are becoming more relevant. These tools can automate and improve the drawing review process so designs are accurate, code compliant and ready for implementation.
The Engineering Drawing Review Process
Traditional Drawing Review
The review process involves multiple stakeholders, architects, engineers and project managers, pouring over each drawing to ensure accuracy and compliance. While thorough, this manual process is time consuming and prone to human error.
Steps in Traditional Review:
Internal Reviews: Preliminary checks are conducted to ensure the drawing aligns with the basic design intent
Draft: Allows stakeholders to identify major inconsistencies early, minimizing significant revisions later.
Final: The final review is a comprehensive evaluation of the refined drawingsSubmit: Contractors submit shop drawings for approval.
Review: Design professionals check for compliance and accuracy.
Feedback: Comments and revisions required.
Resubmit: Revised drawings submitted for final approval.
The manual nature of traditional reviews presents several challenges:
Time-Consuming: Detailed reviews can delay project timelines.
Human Error: Oversights may lead to costly mistakes.
Inconsistency: Variations in reviewer expertise can affect outcomes.
Resource Intensive: Requires significant human capital and coordination.
AI-Powered Solutions for Drawing Reviews
AI technology, powered by machine learning and predictive analytics, can transform the drawing review process. By analyzing structural elements and textual annotations, AI models can identify discrepancies, missing specifications, and non-compliance with industry standards. For instance, an AI system can detect missing rebar details in a foundation drawing or inconsistent dimensions in cross-sectional views.
Textual Annotation Analysis
AI models can analyze textual annotations in engineering drawings. By processing these annotations AI can find potential issues or discrepancies to make the review process more thorough.
Design Specification Verification
AI models can cross reference design specifications with industry standards and project requirements. This verification ensures the future designs are not only accurate but code compliant and compliant with regulations.
Benefits of AI in Quality Control
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Accuracy | AI detects discrepancies that may be overlooked by manual reviews. |
| Increased Efficiency | Automation speeds up the review process, saving time and resources. |
| Predictive Capabilities | AI forecasts potential quality issues, allowing for proactive measures. |
| Cost Savings | Early detection of issues reduces rework and associated costs. |
BuildTwin supports AI-driven project management, providing real-time tracking and automated quality control. Explore how BuildTwin can help you streamline your engineering design reviews today at BuildTwin.
Engineering Drawing Review Checklist
A checklist is key to ensuring engineering drawings meet project requirements, industry standards and are error free. This checklist can be used during the review process for structural, architectural or MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing) drawings to check they are accurate, complete and ready for fabrication or construction.
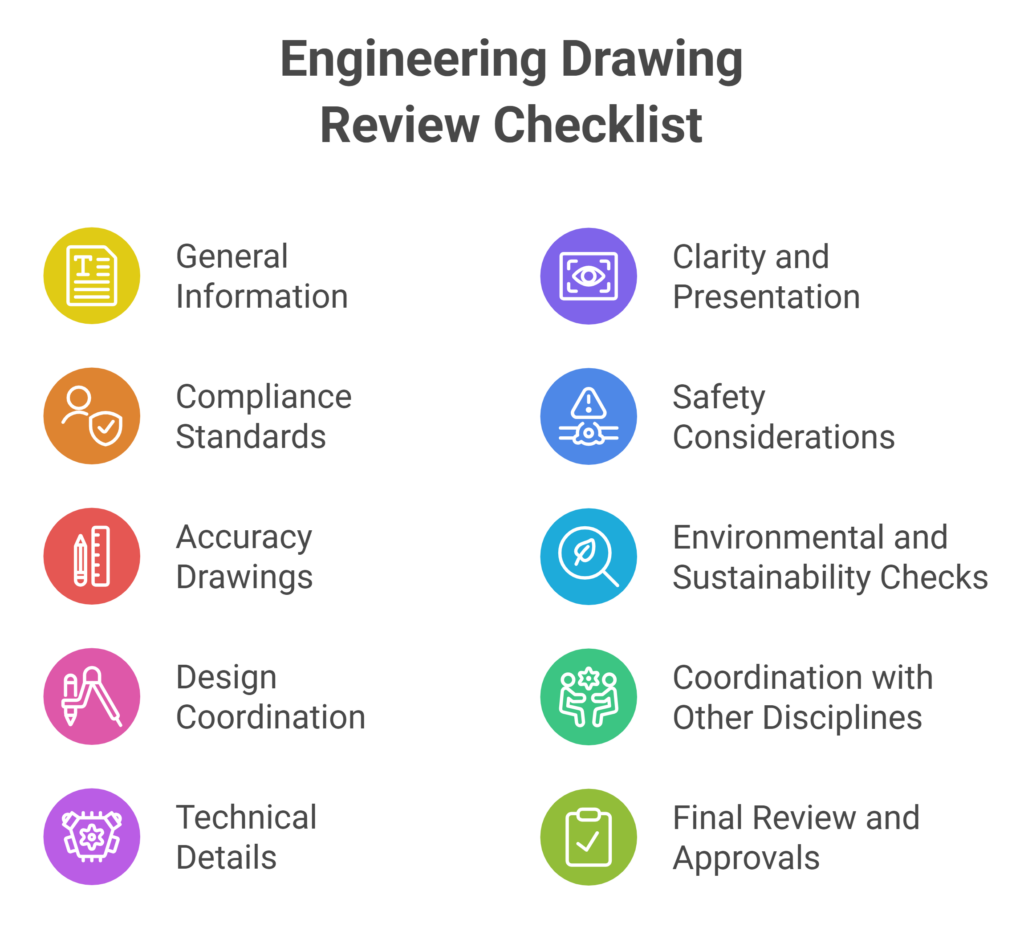
1. General Information & Document Control
Title Block: Ensure that the title block contains all necessary details (e.g., project name, drawing title, drawing number, revision history, date, scale, etc.).
Revision History: Verify that the latest revision is clear and properly documented.
Drawing Date: Confirm that the drawing date is up-to-date.
Project Information: Check if project, client, and consultant names, as well as the drawing’s purpose, are mentioned.
Approvals: Ensure that the drawing has appropriate stamps or signatures for approval (e.g., architect, engineer, contractor).
Document Identification: Ensure the drawing is clearly labeled and identifiable in the project documentation system.
2. Compliance with Standards
Building Codes and Regulations: Check that the drawing adheres to the relevant local and international codes (e.g., ANSI, ISO, Eurocodes, AISC, etc.).
Industry Standards: Ensure compliance with specific standards for the type of drawing (e.g., ASTM for materials, NFPA for fire protection).
Dimensioning and Tolerances: Verify that all dimensions are clear and meet project-specific tolerances (e.g., using ANSI/ASME Y14.5 for GD&T).
3. Accuracy of Drawings
Scale: Ensure that the drawing is at the correct scale and clearly marked.
Accuracy of Dimensions: Check that all dimensions are correct and that measurements align with the design intent.
Clearance and Spacing: Verify that proper clearances are provided between structural elements, MEP systems, and other components.
Level and Elevation: Check if levels, elevations, and floor heights are accurately indicated and consistent.
4. Design and Coordination
Design Intent: Ensure that the drawing reflects the original design intent (architectural, structural, etc.).
Coordinated Systems: Verify that all systems (structural, MEP, etc.) are properly coordinated and do not interfere with each other.
Conflict Detection: Check for potential clashes or conflicts between components, especially in BIM models or multi-disciplinary drawings.
Construction Methods: Confirm that construction methods and materials are appropriate and clearly defined.
Appropriate Symbols and Legends: Ensure all symbols, abbreviations, and terms are clearly defined in a legend or key.
5. Technical Details
Material Specifications: Check that material specifications are clearly mentioned, including type, grade, and finish.
Structural Integrity: Ensure that all load-bearing components, reinforcements, and connections are detailed with enough information.
MEP Systems: Verify that all mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems are well-defined and follow the design parameters.
Details of Joints/Connections: Ensure that joint, weld, and connection details are fully specified.
6. Clarity and Presentation
Legibility: Ensure all text, numbers, and symbols are clear and legible at the scale used.
Line Weights and Styles: Verify that line weights, hatching, and styles are consistent and distinguishable for different components.
Reference Drawings: Ensure that references to other drawings, sections, elevations, or details are correctly noted.
Annotations: Check for correct annotations and ensure they are easy to understand and placed appropriately.
7. Safety Considerations
Safety Features: Verify that safety features, such as fire exits, emergency equipment, or load-bearing safety factors, are clearly shown.
Access and Egress: Ensure that access routes for construction and maintenance are clearly marked and compliant with safety standards.
Risk Assessment: Confirm that potential risks related to design, such as structural instability, have been considered in the design.
8. Environmental and Sustainability Checks
Sustainability Features: Ensure that energy-efficient, sustainable materials, or systems are identified (e.g., renewable energy sources, water management systems).
Environmental Compliance: Check that the design adheres to environmental regulations and standards (e.g., LEED certification).
9. Coordination with Other Disciplines
Architectural Coordination: Verify that the drawing aligns with architectural plans (e.g., room layouts, ceiling heights).
Structural Coordination: Ensure that the structural elements such as beams, columns, and foundations are coordinated with the architectural design.
MEP Coordination: Verify that the mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems are appropriately coordinated with the overall design and do not clash with other systems.
10. Final Review and Approvals
Cross-check with Specifications: Ensure that the drawing aligns with the project’s written specifications.
Team Collaboration: Confirm that the drawing has been reviewed by the relevant teams (e.g., structural engineers, MEP specialists, architects).
Final Approval: Ensure that the drawing has received all required final approvals before being released for construction or fabrication.
AI’s Role in Quality Control
AI models, such as GPT, bring significant advancements to quality control in engineering. They automate the review process, ensuring consistency, accuracy, and compliance. Here’s how AI-driven solutions enhance quality:
Textual Annotation Analysis
In engineering drawings textual annotations provide explanations, dimensions, material specifications and design instructions. But reviewing and checking the clarity and accuracy of these annotations can be time consuming and prone to human error if done manually.
GPT models are great at natural language and can be trained to analyze textual annotations in shop drawings. This allows them to:
Check consistency across multiple drawings to ensure all annotations match the project design specifications.
Identify ambiguous or incomplete instructions that might lead to misunderstandings during construction.
Flag discrepancies between design documents and textual annotations that put the project at risk.
Example: If an engineering drawing has one annotation that specifies a steel grade at one point and another annotation elsewhere in the document that uses a different grade, AI will flag this as a discrepancy that needs to be fixed before moving forward.
Automating the review process allows project managers and engineers to ensure the review process is thorough and quality control is done early in the development of the project and reduces costly revisions later.
Learn how BuildTwin is helping improve project management with AI-powered reviews at BuildTwin.
Design Specification Verification
One of the most critical part of the drawing review process is to verify the design specifications in the shop drawings are code compliant and project requirements. This crucial part can be time consuming especially when dealing with large projects that involves multiple documents and specifications.
AI can help with this by cross referencing design specifications with established standards and project guidelines. This can be broken down into:
Automated cross-referencing: AI can be trained to compare the shop drawing against industry standards (ISO, DIN, AISC, Eurocodes) and project specific requirements.
Identifying non-compliance: By understanding the text based specifications and project parameters, AI can flag potential non-compliance such as incorrect dimensions, material selection or missing elements that don’t match the design construction standards.
Efficient updates and corrections: When GPT finds discrepancies between specifications and drawing review process it can suggest corrections or ask experts to review to avoid delays.
For instance AI can automatically check if a structure on a structural drawing meets the correct load bearing specifications as per project management documentation. If it finds a mismatch it will alert the design team before it becomes a costly mistake on site.
By integrating and using AI in quality control the risk of errors in shop drawing reviews is minimized and compliance and project management improves.
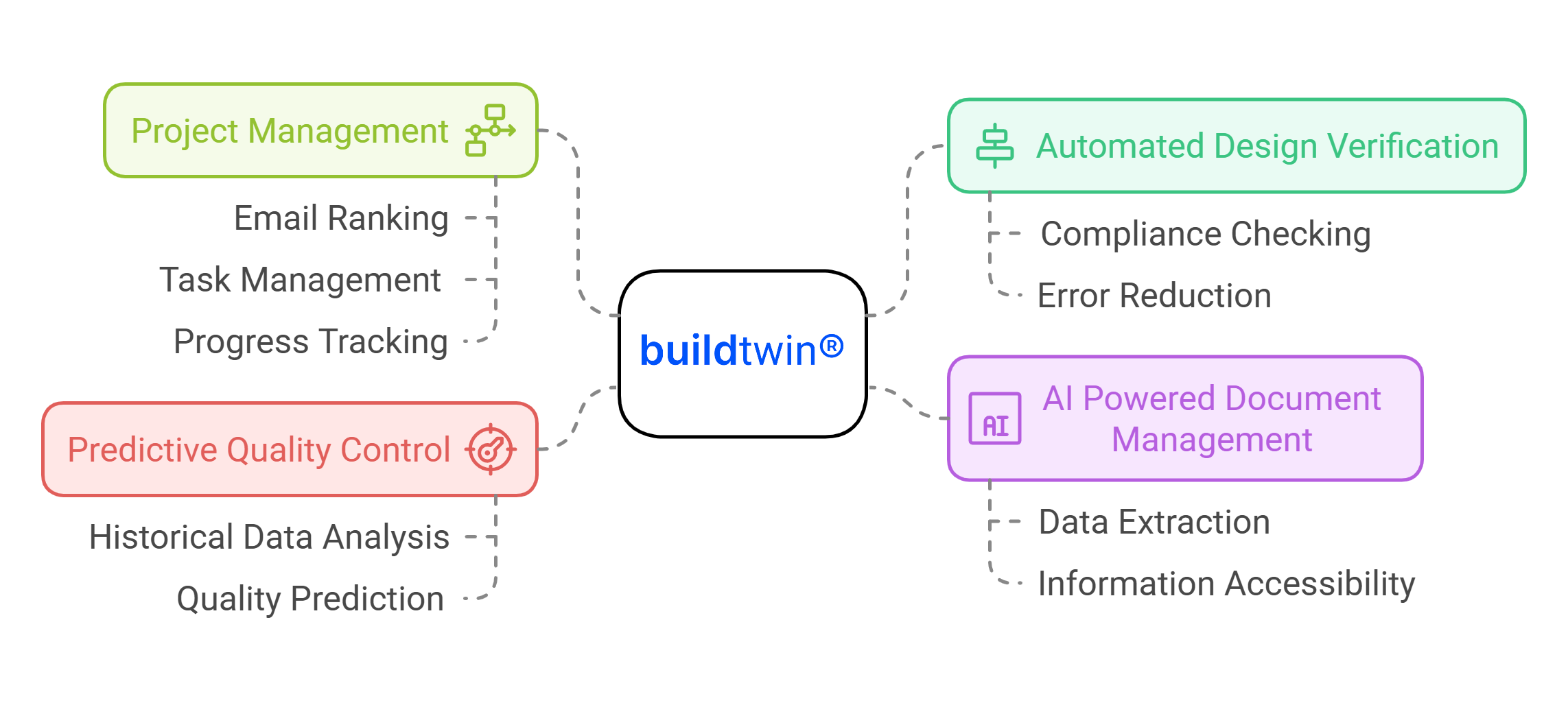
How AI Reviews Engineering Drawings
AI-powered tools ease the engineering drawing review process by automating critical tasks and providing insights based on historical and real-time data. Here’s how AI enhances the review process:
Prioritizes Emails and Tasks: Ensures critical communications and assignments are addressed promptly.
Summarizes Messages: Extracts key points from lengthy conversations.
Manages Documents: Organizes, labels, and consolidates essential files.
Analyzes Drawings: Flags inconsistencies and annotates key elements.
Predicts Issues: Uses historical data to forecast errors or delays.
What Information Does AI Need for Drawing Reviews?
For AI to effectively review engineering drawings, it requires a consolidated data source from multiple communication and documentation platforms, including:
Emails and Chats: To analyze design discussions, feedback, and revisions.
Project Management Tools: To track tasks, deadlines, and workflows.
Documentation Systems: To access shop drawings, specifications, and project guidelines.
To enable seamless integration, it’s essential to use an AI software with CDE (Common Data Environment) capabilities. This ensures:
Data Consolidation: AI can connect to various tools and centralize data in one platform.
Streamlined Workflows: Enhances collaboration and improves the efficiency of the review process.
Understanding GPT and Its Capabilities
Overview of GPT Models in Engineering
Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPT) are advanced AI models that have gained popularity in recent years for their ability to generate and understand human-like text. Originally used in natural language processing tasks, GPT models have expanded to design analysis. By leveraging massive amount of training data, GPT models are now used to interpret and review engineering drawings to automate tasks such as error detection, compliance checking and quality control. With increasing complexity of engineering designs, GPT technology is a promising solution to streamline processes, reduce human error and improve efficiency in engineering workflows.
These capabilities enable GPT to support various engineering tasks, from drafting reports and summarizing design documents to understanding technical jargon.
GPT’s ability to understand context, identify key terms and generate text enables it to communicate within engineering teams.
For instance, GPT can be used to generate detailed explanations of engineering designs, propose revisions, or even suggest solutions to common design problems by interpreting the underlying documentation.
Moreover, GPT is well-suited to do review and analysis of shop drawings and design specifications, identifying inconsistencies and proposing improvements. However, it is important to note that GPT’s understanding is primarily text-based, meaning its strengths lie in working with written or verbal information, rather than in interpreting raw design data directly from visual mediums.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the use cases, there are several challenges to widespread adoption of AI in engineering drawing reviews:
Limitations in Visual Data Interpretation: Although GPT is good at natural language understanding, it has limitations when it comes to visual data. Engineering drawings whether structural, architectural or mechanical contain complex visual information such as shapes, dimensions and spatial relationships that are not textual. GPT can process textual annotations or labels within a drawing but cannot “see” or fully understand the intricate visual details that are critical in design analysis.
For example, GPT cannot directly interpret graphical elements such as the precise placement of beams or the scaling of dimensions. These visual cues are essential for tasks like collision detection or verifying the structural integrity of components, areas where specialized AI models, like those using computer vision or BIM (Building Information Modeling) technology, excel.
Combining GPT’s natural language strengths and techniques with computer vision models would enable a more comprehensive approach to design analysis and quality control.
Integration with Existing Systems: Incorporating AI into established workflows and software can be complex and resource-intensive.
Data Quality and Availability: AI models require high-quality, annotated data for training, which may not always be available.
Conclusion
While GPT models offer significant potential in automating and enhancing various aspects of the engineering drawing review process, their current capabilities are primarily focused on textual analysis. As AI technology advances its role in quality control, design construction and project management will expand and engineering will be more productive, efficient and accurate.
At BuildTwin, we understand the importance of leveraging AI to revolutionize the drawing review process. Our platform combines cutting-edge AI tools with a robust ERP system to enhance accuracy, streamline reviews, and optimize design and construction workflows. Discover how our AI-driven solutions can transform your engineering projects.



